Anode and Cathode in Electrolysis
And in order to separate the different gases formed at the cathode and anode respectively the use of a. According to the equations for the two half-reactions the indicator should turn yellow at the anode and blue at the cathode.
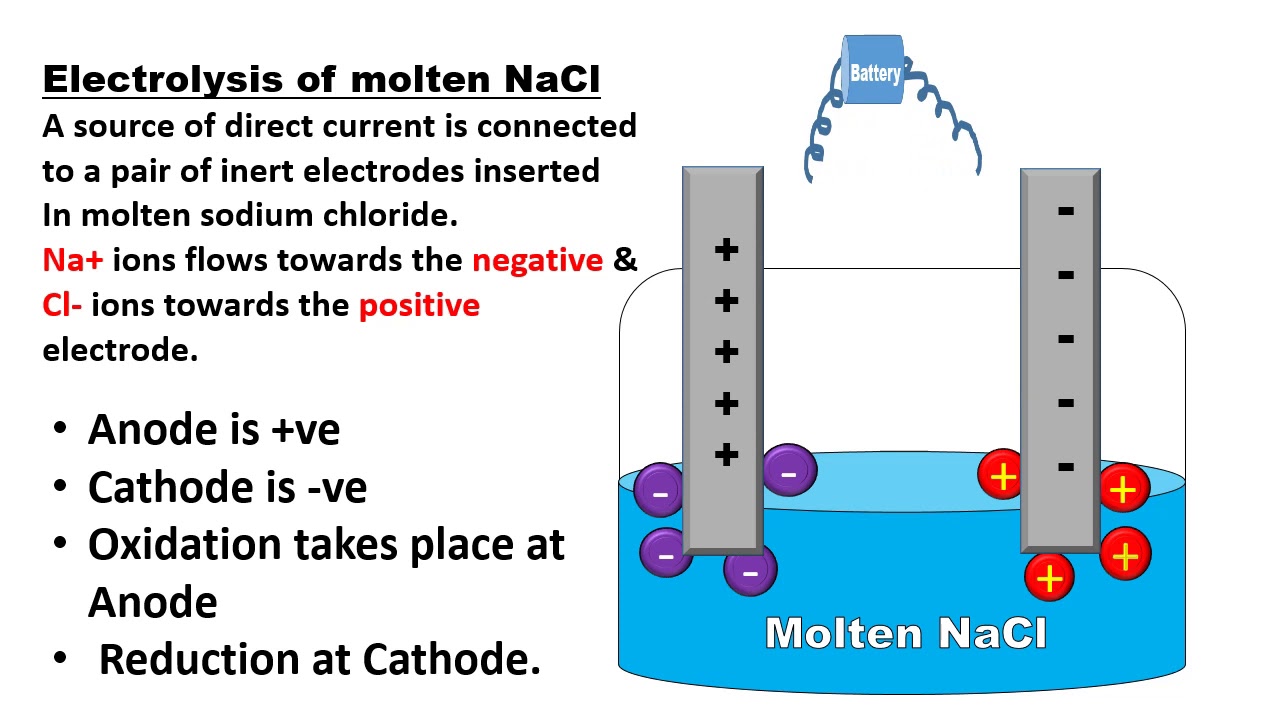
What Is Electrolytic Cell Electrochemistry Chemistry Basics Chemistry
2 H 2 O O 2 4 H 4 e-Faradays Law.

. The cathode is made of pure copper or a support metal such as stainless steel. Before we learn about the terms cathode and anode it is important to understand what an electrode is. Electrolysis is used to drive an oxidation-reduction reaction in a direction in which it does not occur spontaneously.
The main components of an electrochemical cell are the anode the cathode and the electrolyte. The slideshow shows what happens. The H ions called cations move toward the cathode negative electrode and the OH- ions called anions move toward the anode positive electrode.
The bubbles are easily seen. At the cathode water is split to form H2 and releases hydroxide anions which pass through the diaphragm and recombine at the anode to form O2. When voltage is applied hydrogen is produced at the cathode and oxygen at the anode.
Bubbles of oxygen gas O form at the anode and bubbles of hydrogen gas H 2 2. The electrolysis can be done using two weighed copper strips. Half reactions of electrolysis in the presence of a base are-.
Form at the cathode. According to the general definition an electrode is a substance that helps in electricity conduction wherein the electric current either leaves or enters the non-metallic medium such as an electrolytic cell. Electrons flow in the external circuit from the.
In electrochemical cells the cathode is the site where reduction occurs. Electrolysis process by which electric current is passed through a substance to effect a chemical change. The electrode where reduction is occurring is represented by a positive sign.
The electrolysis takes place at a much lower potential than pure water 24V. Water Electrolysis in the Presence of a Base pH higher than 7 Additional hydroxyl ions release their electrons to anode while electrons at the cathode oxidize water molecules near it. Reduction occurs at the cathode.
Electroplating and electrolysis welding cathodic protection. 2 H 2 O 2 e-H 2 2 OH-Anode. Electrolysis is a technique that uses a direct electric current DC.
Published continuously from 1902 to the present JES remains one of the most highly-cited journals in electrochemistry and solid-state science and technology. The anode is a positively charged electrode. Electrolysis involves passing an electric current through either a molten salt or an ionic solution.
Anions move through the barrierbridge toward the electrode where oxidation is occurring. Here electrons are released from the electrode and the surrounding solution is reduced. While the basis remains the same different electrolysis methods including polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzer alkaline electrolyzer and solid.
The anode is the site where. The less noble metal in a reaction will be the anode. Electrolysis involves the manipulation of chemical reactions based on their electric potential.
Then they head towards the cathode. The process is carried out in an electrolytic cell an apparatus consisting of positive and negative electrodes held apart and dipped into a solution containing positively and. The splitting occurs in two partial reactions that take place at the two electrodes cathode - and anode in the electrolysis cell.
In practice electrolysers consist of several interconnected electrolysis cells also called stacks. The ions are forced to undergo either oxidation at the anode or reduction at the cathode. The electrolyte conducts electricity for electrolysis to occur.
The anode consists of an unrefined sample of the metal. Releasing electrons to the anode. The two common terms we hear is cathode and anode.
So what does that mean. Water electrolysis relies on the application of an electric current through an anode and cathode inserted in the electrolyte to provide the required energy to break the hydrogen and oxygen bond. During electrolysis the anode loses mass as copper dissolves and the cathode gains mass as copper is deposited.
The process of electrolysis sees electrons being stripped from the anode. A cathode is a negatively charged electrode. The anode and cathode are separated by a diaphragm separating hydrogen and oxygen gases and preventing them from mixing up again.
Low-temperature CO2 electrolysis represents a potential enabling process in the production of renewable chemicals and fuels notably carbon monoxide formic acid ethylene and ethanol. Reversible hydrogen electrode RHE is required to split water into H 2 and O 2However both the cathode and anode reactions involve multiple electron transfer steps and additional energy is needed to overcome kinetic obstacles and accelerate electron transfer resulting in. Likewise the cathode reduces sodium ions Na which accept electrons from the cathode and deposits on the cathode as sodium.
The chemical change is one in which the substance loses or gains an electron oxidation or reduction. Commercially electrolytic cells are used in electrorefining and electrowinning of several non-ferrous metals. The anode and cathode of a voltaic cell are separated into two half-cells and connected by a metal wire.
In the electrolysis process electrolyzers use electricity for water-splitting. Regardless of the electrolyte media the standard thermodynamic potential of 123 V vs. The more noble metal in the reaction will always be the cathode.
The cathode is the current that leaves the electrodes or cathode is a result of reduction reaction taking place in an electrolyte mixture. Most electrolysis problems are really stoichiometry problems with the addition of an amount of electric current. Cathode Anode and Electrolyte.
An electrochemical reaction occurs which is 7080 efficient and is the most established well-known commercially available technology for water-splitting. This is to confirm that the mass gained at the cathode is. JES is the flagship journal of The Electrochemical Society.
To flow when a voltage is applied. The reaction between the two elements in an electrolytic cell is a reduction-oxidation -- or redox -- reaction.

Electrolysis Process On Passing Electric Current The Cations Move Towards The Cathode And Get Deposited Piscinas De Agua Salada Escuela De Natacion Piscinas

Electrolysis Of Copper Sulfate Solution With Impure Copper Anode And Pure Copper Cathode Copper Purification Technology Educat Pure Products Copper Solutions

Look4chemistry Electrolytic Cell Electrochemistry Cell Positive And Negative

Electrochemistry Featuring Electrolysis And Fuel Cells Chemistry Classroom Electrochemistry Chemistry Lessons
No comments for "Anode and Cathode in Electrolysis"
Post a Comment